How To Calculate Payment Amount On A Loan
adminse
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
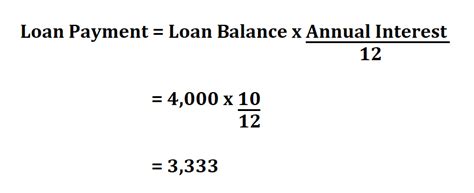
Table of Contents
Decoding Loan Payments: A Comprehensive Guide to Calculating Your Repayment Amount
What if understanding loan payment calculations could save you thousands of dollars over the life of a loan? Mastering these calculations empowers you to make informed borrowing decisions and avoid costly financial pitfalls.
Editor’s Note: This article on calculating loan payments was published today, providing you with the most up-to-date information and formulas to accurately determine your repayment obligations.
Why Loan Payment Calculations Matter:
Understanding how loan payments are calculated is crucial for responsible borrowing. It allows you to compare loan offers effectively, negotiate better terms, and avoid unexpected surprises. Whether you're considering a mortgage, auto loan, personal loan, or student loan, accurate calculation empowers you to make informed financial decisions, ensuring you choose the loan that best fits your budget and financial goals. The ability to calculate payments also helps in budgeting effectively, preventing missed payments and potential damage to your credit score.
Overview: What This Article Covers:
This article will provide a detailed explanation of the core principles behind loan payment calculations, focusing on the most common methods. We will explore the impact of interest rates, loan terms, and principal amounts on your monthly payments. We'll delve into various scenarios, including loans with different compounding frequencies and those with additional fees. Finally, we'll provide practical tips and tools to help you easily calculate your loan payments.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights:
This article draws upon established financial principles and widely accepted formulas for loan amortization. The information presented is based on standard mathematical models used by lending institutions and financial calculators. We have cross-referenced our calculations with multiple sources to ensure accuracy and provide you with reliable, actionable information.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Loan Amortization: A breakdown of how loan payments are allocated between principal and interest over the loan's lifespan.
- The Impact of Interest Rates: How changes in interest rates significantly affect monthly payments and total interest paid.
- Loan Term's Influence: Exploring the relationship between loan duration and the size of monthly payments.
- Calculating Payments with Different Compounding Frequencies: Understanding the variations in payment calculations based on how interest is compounded (monthly, quarterly, annually).
- Incorporating Fees and Charges: Adjusting calculations to account for upfront fees, origination fees, and other loan-related expenses.
- Using Online Calculators and Software: Leveraging readily available resources to simplify the calculation process.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion:
Now that we've established the importance of understanding loan payment calculations, let's delve into the specifics of how these calculations are performed.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Loan Payment Calculations:
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
The core of loan payment calculation lies in understanding loan amortization. Amortization is the process of gradually paying off a loan over time through regular payments. Each payment consists of two parts: principal and interest. The principal is the original loan amount, while the interest is the cost of borrowing money. In the early stages of a loan, a larger portion of each payment goes towards interest, while as the loan matures, more of each payment goes towards the principal.
2. The Standard Amortization Formula:
The most widely used formula for calculating loan payments is:
M = P [ i(1 + i)^n ] / [ (1 + i)^n – 1]
Where:
- M = Monthly payment
- P = Principal loan amount
- i = Monthly interest rate (Annual interest rate divided by 12)
- n = Total number of payments (Loan term in years multiplied by 12)
3. Applications Across Industries:
This formula finds widespread application across various lending sectors. Mortgages, auto loans, personal loans, and student loans all utilize variations of this formula to determine monthly payments. The specific variables may change depending on the type of loan and the lender's policies, but the underlying principle remains the same.
4. Challenges and Solutions:
One common challenge is accurately determining the monthly interest rate. Ensure you convert the annual interest rate to a monthly rate before applying the formula. Another challenge is understanding the impact of fees. These fees should be incorporated into the principal amount to obtain a more realistic monthly payment.
5. Impact on Innovation:
The development of sophisticated financial software and online calculators has simplified the process of loan payment calculation. These tools often incorporate additional variables, such as prepayment penalties and variable interest rates, offering more accurate and comprehensive payment estimates.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion:
Calculating loan payments isn’t just about plugging numbers into a formula; it's about understanding the financial implications of your borrowing decisions. By mastering this calculation, you gain control over your finances, enabling you to make informed choices and avoid costly mistakes.
Exploring the Connection Between Interest Rates and Loan Payments:
The interest rate is arguably the most significant factor influencing loan payments. A higher interest rate translates directly into larger monthly payments and a higher total amount paid over the loan's life. Conversely, a lower interest rate reduces your monthly burden and the overall interest expense.
Key Factors to Consider:
- Roles and Real-World Examples: Consider two identical loans, one with a 5% interest rate and another with a 7% interest rate. The higher rate will result in substantially higher monthly payments and a greater total interest cost.
- Risks and Mitigations: High interest rates pose a significant risk of financial strain. Mitigation strategies include securing a loan with a lower interest rate, reducing the loan term, or increasing your down payment.
- Impact and Implications: The interest rate fundamentally shapes the affordability and overall cost of a loan. Understanding its impact allows for more informed financial planning.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection:
The relationship between interest rates and loan payments underscores the critical importance of shopping around for the best rates. Careful comparison of loan offers, considering both interest rates and fees, is vital for minimizing the financial burden of borrowing.
Further Analysis: Examining Loan Terms in Greater Detail:
The loan term, or the length of time you have to repay the loan, also significantly influences your monthly payments. A longer loan term results in lower monthly payments, but you will pay significantly more interest over the life of the loan. A shorter loan term results in higher monthly payments but significantly less interest paid overall.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) Section:
Q: What is the difference between simple interest and compound interest?
A: Simple interest is calculated only on the principal amount, while compound interest is calculated on the principal plus accumulated interest. Most loans use compound interest.
Q: How do I account for additional fees in my loan payment calculation?
A: Add any upfront fees or origination fees to the principal amount before using the amortization formula.
Q: Can I use a loan calculator to verify my calculations?
A: Yes, many free online loan calculators are available to verify your calculations and explore different scenarios.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Understanding Loan Payment Calculations:
- Shop Around: Compare loan offers from different lenders to find the best interest rate and terms.
- Use a Loan Calculator: Utilize online tools to easily calculate payments under various scenarios.
- Understand the Amortization Schedule: Review the breakdown of principal and interest payments over the loan's life.
- Negotiate: Try to negotiate a lower interest rate or better terms with the lender.
- Budget Wisely: Ensure that your monthly loan payment fits comfortably within your budget.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights:
Mastering loan payment calculations empowers you to take control of your finances. By understanding the intricacies of amortization, interest rates, and loan terms, you can make informed borrowing decisions, minimizing financial risks and maximizing your financial well-being. Remember, informed choices lead to responsible borrowing and long-term financial success.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Minimum Pip Coverage In Florida
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Slope For Pipe Sizes 3 To 6
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Cover For Pipework Installed Underneath A Driveway
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Depth For Pipes Below Grade
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Is The Minimum Term For Pip
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Calculate Payment Amount On A Loan . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.