What Is The Minimum Slope For Pipe Sizes 3 To 6
adminse
Apr 06, 2025 · 8 min read
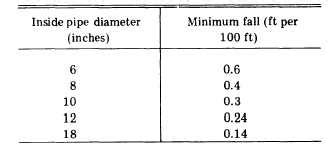
Table of Contents
What's the Minimum Slope for Pipes Sizes 3" to 6"? A Comprehensive Guide to Gravity Drainage
What if ensuring efficient drainage hinged on understanding the minimum slope for pipes of various sizes? This seemingly simple factor significantly impacts the effectiveness and longevity of plumbing and drainage systems.
Editor’s Note: This article on minimum pipe slopes for sizes 3" to 6" was published today, providing up-to-date information on best practices and relevant building codes. This comprehensive guide will help plumbers, contractors, and homeowners understand the crucial role of proper pipe slope in maintaining efficient drainage systems.
Why Minimum Pipe Slope Matters: Relevance, Practical Applications, and Industry Significance
The minimum slope of a pipe, often expressed as a gradient (rise over run), is critical for ensuring gravity-driven flow of wastewater and stormwater. Insufficient slope leads to blockages, slow drainage, and potential backups, causing property damage, health hazards, and costly repairs. Conversely, excessively steep slopes can lead to accelerated erosion and premature wear on the pipes. Understanding and adhering to the recommended minimum slopes for pipes sizes 3" to 6" is essential for the successful design and installation of reliable and efficient drainage systems across residential, commercial, and industrial settings. This impacts not only the immediate functionality but also long-term maintenance costs and environmental considerations.
Overview: What This Article Covers
This article will delve into the specifics of determining the minimum slope for pipes ranging from 3 inches to 6 inches in diameter. It will explore the factors influencing slope recommendations, including pipe material, flow rate, and applicable building codes. We will also examine the consequences of improper slopes and provide practical guidance for achieving optimal drainage performance. The article concludes with a FAQ section and actionable tips for ensuring correct pipe installation.
The Research and Effort Behind the Insights
This article is the result of extensive research, drawing upon established plumbing codes (such as the International Plumbing Code – IPC, and local variations), engineering manuals, and industry best practices. Data regarding flow dynamics in pipes of various sizes and materials have been analyzed to present accurate and reliable information. The information provided is intended to be a guide and should be complemented by consultation with relevant professionals for specific project needs.
Key Takeaways:
- Definition and Core Concepts: A clear explanation of pipe slope, its importance, and the units used for its measurement.
- Practical Applications: Illustrative examples of minimum slope requirements for different pipe sizes (3", 4", 5", 6") in various applications.
- Challenges and Solutions: Common problems encountered due to incorrect pipe slope and effective strategies to prevent them.
- Future Implications: The ongoing relevance of understanding proper pipe slope in the context of sustainable infrastructure and evolving building regulations.
Smooth Transition to the Core Discussion
Having established the importance of proper pipe slope, let's explore the key aspects impacting the minimum slope requirements for 3" to 6" pipes. We'll examine the influencing factors and provide practical recommendations based on widely accepted standards.
Exploring the Key Aspects of Minimum Pipe Slope
1. Definition and Core Concepts:
Pipe slope is defined as the vertical drop per unit of horizontal distance. It’s usually expressed as a ratio or percentage (e.g., 1/4 inch per foot, or 2%). This means for every foot of horizontal distance, the pipe should drop by the specified amount vertically. Accurate measurement and consistent slope are crucial for efficient gravity flow. The units used (inches per foot or percentage) may vary depending on the region and the specific plumbing code.
2. Applications Across Industries:
The minimum slope requirements apply broadly across various sectors:
- Residential Plumbing: Wastewater drainage from sinks, toilets, showers, and other fixtures.
- Commercial Buildings: Drainage systems for larger facilities like hotels, office complexes, and restaurants.
- Industrial Applications: Handling wastewater from manufacturing processes or larger-scale drainage projects.
- Stormwater Management: Municipal drainage systems for handling rainwater runoff.
3. Challenges and Solutions:
- Insufficient Slope: Leads to slow drainage, blockages, and potential sewer backups. Solutions include re-grading the pipe run or using a larger diameter pipe to improve flow.
- Excessive Slope: Can cause erosion and damage to the pipe over time. Solutions include adjusting the slope to the recommended minimum.
- Improper Installation: Incorrect installation techniques can lead to dips and variations in slope. Solutions include careful planning, precise measurement, and proper installation methods.
- Material Limitations: Different pipe materials (PVC, cast iron, etc.) may have specific recommendations for minimum slopes.
4. Impact on Innovation:
Ongoing advancements in pipe materials and construction techniques aim to improve drainage efficiency and reduce the risk of blockages. However, the fundamental principle of maintaining a minimum slope remains crucial regardless of technological advancements.
Closing Insights: Summarizing the Core Discussion
Maintaining the correct minimum slope for pipes from 3" to 6" is not merely a detail but a cornerstone of functional and long-lasting drainage systems. Ignoring this crucial aspect can lead to costly repairs, health hazards, and environmental problems. By adhering to the recommended slopes and employing proper installation techniques, professionals can ensure efficient, reliable, and sustainable drainage solutions.
Exploring the Connection Between Pipe Diameter and Minimum Slope
The diameter of the pipe directly impacts the minimum slope required for efficient drainage. Larger diameter pipes generally require a gentler slope due to their increased capacity to handle higher flow rates. Conversely, smaller diameter pipes need a steeper slope to compensate for their reduced capacity and avoid blockages.
Key Factors to Consider:
Roles and Real-World Examples:
- 3-inch Pipe: Often used for smaller drainage lines, requiring a steeper slope (typically 1/4 inch per foot or more, depending on the code) to maintain adequate flow. This is common for bathroom drains or smaller branch lines.
- 4-inch Pipe: Commonly used for main drainage lines in residential settings, often requiring a slightly less steep slope (possibly 1/8 inch per foot, though this varies by code).
- 5-inch and 6-inch Pipes: Used for larger drainage lines in commercial or industrial settings, or for main sewer lines, requiring even gentler slopes (potentially as low as 1/8 inch per foot or even less). The specific requirements depend heavily on the expected flow rate and local code.
Risks and Mitigations:
- Blockages: Insufficient slope increases the risk of blockages due to slower flow and the accumulation of solids. Mitigation involves ensuring the correct slope, using appropriate pipe materials, and regular maintenance.
- Erosion: Excessive slope can lead to erosion of the pipe material over time. Mitigation involves adhering to the recommended minimum slope.
- Backups: Insufficient slope can cause backups into fixtures and fittings. Regular maintenance and inspection help in early detection and prevention.
Impact and Implications:
The choice of pipe diameter and its corresponding minimum slope directly impacts the overall efficiency and reliability of the drainage system. Incorrect choices can have significant long-term consequences, affecting both the immediate usability and the lifespan of the system.
Conclusion: Reinforcing the Connection
The relationship between pipe diameter and minimum slope is fundamental to achieving efficient gravity drainage. Understanding this connection is crucial for selecting the appropriate pipe size and maintaining the correct slope during installation.
Further Analysis: Examining Pipe Material in Greater Detail
Pipe material significantly affects its performance, durability, and the recommended minimum slope. Different materials have varying resistance to flow, affecting the required slope for optimal drainage.
- PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride): A common material due to its low cost, durability, and resistance to corrosion. PVC pipes generally require slopes that are consistent with those outlined in building codes.
- Cast Iron: A traditional but heavier and more expensive material. Its smoother interior can allow for slightly gentler slopes in some cases, but this is highly dependent on the pipe's age and condition.
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): A flexible and durable material often used in underground applications. The flexibility allows for easier installation in challenging terrains but specific slope requirements depend on the pipe’s properties.
- Clay Pipes: Less common now but still found in older infrastructure. These often require stricter slope adherence due to their irregular interior surfaces.
FAQ Section: Answering Common Questions About Minimum Pipe Slopes
Q: What happens if the minimum slope is not met?
A: Insufficient slope leads to slow drainage, blockages, sewer backups, and potential damage to the drainage system and property.
Q: Can I use a larger diameter pipe to compensate for a flatter slope?
A: To a degree, yes. A larger diameter pipe can handle higher flow rates with a gentler slope, but it's still crucial to meet the minimum slope requirements specified by codes to avoid problems.
Q: Are there regional variations in minimum slope requirements?
A: Yes, building codes and regulations vary regionally. Always consult your local building codes for precise requirements.
Q: How is pipe slope measured on-site?
A: A laser level or a water level are commonly used to accurately measure the slope and ensure consistent grading during pipe installation.
Practical Tips: Maximizing the Benefits of Proper Pipe Sloping
- Understand the Basics: Familiarize yourself with the definitions and units of measurement for pipe slope.
- Consult Local Codes: Always check your local building codes for specific minimum slope requirements.
- Accurate Measurement: Utilize appropriate tools (laser levels, water levels) for precise measurement.
- Consistent Grading: Maintain consistent slope throughout the entire pipe run.
- Proper Installation: Follow recommended installation practices to prevent dips or variations in slope.
- Regular Inspection: Regularly inspect the drainage system for any signs of blockage or malfunction.
Final Conclusion: Wrapping Up with Lasting Insights
Understanding and adhering to the minimum slope requirements for pipes sizes 3" to 6" is paramount for the efficient and reliable operation of drainage systems. This seemingly small detail has far-reaching implications for the functionality, longevity, and cost-effectiveness of any plumbing or drainage project. By implementing the recommendations outlined in this article, stakeholders can ensure the long-term success and sustainability of their drainage infrastructure. Careful planning, accurate measurement, and adherence to building codes are essential for achieving optimal drainage performance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Credit Percentage Usage
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Percentage Of Credit Usage Is Good
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Percentage Should Credit Utilization Be
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Is The Ideal Credit Utilization Ratio
Apr 07, 2025
-
Is 10 Percent Credit Utilization Good
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Minimum Slope For Pipe Sizes 3 To 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.